European Telecommunications Standards Institute and related standards
European Telecommunications Standards Institute and related standards classification

1. Basic situation
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) was founded in 1988 by the European Council of Posts and Telecommunications (CEPT) and is headquartered in the Sophia Science and Technology Park in France. ETSI is recognized by the European Commission and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) Secretariat and is responsible for Europe-wide information and communication technology standardization work. With the development of the times, the organization has now developed into the world's leading information and communication technology (ICT) international standardization organization. ETSI has played an important role in promoting digital transformation in multiple areas, such as 5G, cybersecurity, Internet of Things, machine-to-machine communications, etc.
As a European standards organization, ETSI cooperates with many forums, alliances, international and regional standard-setting organizations around the world, and has become a founding partner of international cooperation projects 3GPP and oneM2M. ETSI's strength lies in its vast network of experts and innovators who work together to enable interoperability in multi-vendor, multi-network, multi-service environments.
ETSI's organizational structure has the General Assembly as the highest decision-making level, responsible for policy and management. There are two annual meetings, and more than 71% of the votes cast make the decision effective. The Board of Directors manages daily operations and ensures the execution of decisions. Technical bodies (Technical Bodies), including Technical Committees (TCs) and their subcommittees, ETSI Project Teams (PTs) and ETSI cooperation project teams, are responsible for the formulation of standards in various fields, both permanent and temporary projects Group. The Secretariat handles administrative coordination matters. In addition, ad hoc committees respond to specific needs and include non-voting members to ensure an open and collaborative organization.
ETSI member organizations come from more than 60 countries on five continents, with a total of more than 900 (see picture), including 18 member organizations from China (see table below), 143 from Germany, 98 from France, 115 from the United Kingdom, and 58 from the United States. . Membership categories span private companies, research institutions, academia, government and public institutions, and social stakeholders. 27% of its members are small, medium and micro enterprises, and about 20% of the membership growth occurred in the past 10 years.
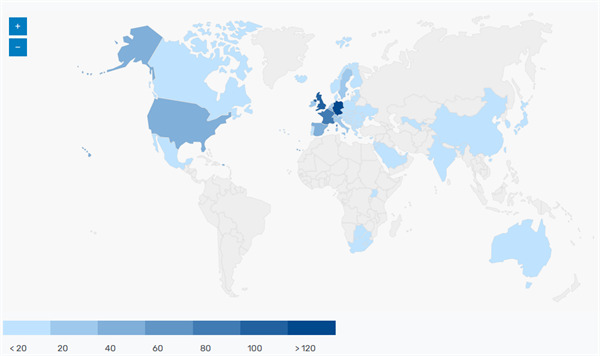
Figure 1: Global distribution map of European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) members
More than 100 technical groups under ETSI have held more than 4,000 meetings, including seminars, summits and webinars, with more than 32,000 people participating offline and more than 39,000 people participating online; on average, more than 50 meetings are held every year and operational testing activities. By participating in ETSI's conferences and events and using ETSI's standards, suppliers and manufacturers can quickly enter the European market.
serial number |
Company Name |
category |
Remark |
1 |
Asia Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
service provider |
|
2 |
Hong Kong Applied Science and Technology Research Institute |
public research institution |
|
3 |
Beijing Xiaomi Mobile Software Co., Ltd. |
manufacturer |
|
4 |
Beijing Jiaotong University |
University |
|
5 |
Beijing Huahuan Electronics Co., Ltd. |
other |
Small and medium-sized enterprises |
6 |
China Academy of Information and Communications Technology |
public research institution |
|
7 |
China Thiel Laboratory |
manufacturer |
|
8 |
China Telecom |
Network operators |
|
9 |
ZTE Corporation |
manufacturer |
|
10 |
Beijing Communications Technology Experimental Institute |
other government agencies |
|
11 |
glory |
manufacturer |
|
12 |
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd |
manufacturer |
|
13 |
Hytera Communications Co., Ltd. |
manufacturer |
|
14 |
OPPO |
manufacturer |
|
15 |
quantum network |
Network operators |
Small and medium-sized enterprises |
16 |
Shenglu Communications |
manufacturer |
|
17 |
Tuwei wireless |
service provider |
Small and medium-sized enterprises |
18 |
ZTE Corporation |
manufacturer |
Table 1: Chinese member organizations of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)
2. Relevant standards
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an important participant in the field of international standardization. It has released a total of 53,000 standards, more than 1,800 standards are released every year, and the website files are downloaded more than 19 million times. As a non-profit organization, ETSI's goal is to promote telecommunications and technology standardization in Europe and internationally to support interoperability and harmonization. ETSI's operating model and mission encourage openness and broad participation, which includes making standards as accessible as possible so that industry, research institutions, governments and other stakeholders can adopt and implement them. (This public account has compiled a catalog of relevant standards, please leave a message for consultation).
The standards released by ETSI cover standard cases that have contributed to the success of global key technologies such as GSMTM, 3G, 4G, 5G, DECTTM, etc., as well as many information and communications technology (ICT). With the advancement of technology, it is gradually focusing on digital transformation fields such as 5G, network security, machine-to-machine communications, edge computing, network virtualization, artificial intelligence, quantum security encryption, radio, augmented reality, blockchain and smart cities.
(1) Classification according to file type
The types of standard documents published by ETSI include specifications, standards, reports and guidelines, each type has its specific purpose:
1. European Standards (EN): designed to meet the unique needs of Europe and need to be converted into national standards, or used when drafting in accordance with the standard setting requirements of the European Commission (EC)/European Free Trade Association (EFTA). EN is drafted by a technical committee and approved by ETSI, the European national standards organization. In addition, ETSI also develops harmonized standards (HS) based on EC standards to provide the necessary technical details to achieve the "basic requirements" of the EC directive.
2. European standardization achievements: In addition to European standards, any other technical specifications adopted by the European Standardization Organization for repeated or continuous application, and compliance is not mandatory.
3. ETSI Standard (ES): used when the document contains technical requirements. ES is submitted to all ETSI members for approval.
4. ETSI Guidelines (EG): used to provide overall guidance to ETSI in handling specific technology standardization activities. Submit to all ETSI members for approval.
5. ETSI Technical Specification (TS): Used when the document contains technical requirements and rapid availability is critical. The TS is approved by the technical committee that drafted it.
6. ETSI Technical Report (TR): Used when the document contains explanatory material. A TR is approved by the technical committee that drafts it.
7. ETSI Special Report (SR): used for various purposes, including public information for reference. The SR is approved by the technical committee that produced it.
8. ETSI Group Specifications (GS): Produced and approved within our Industry Specification Groups (ISGs), providing technical requirements, explanatory material, or both.
9. ETSI Group Report (GR): ETSI's deliverables contain only informational elements and are approved and released by the Industry Standards Group.
(2) Classification according to the fields involved
1. Home & Office Environment (Home & Office)
In response to the "smart home" and "smart office" trends, standardization work focuses on three aspects: home and office wireless technology, home and office interconnection, and home and office demand specifications, covering quality of service (QoS) and security requirements.
2. Better Living with ICT
While promoting the advancement of social and business communication methods, pay attention to reducing potential negative social impacts. We are committed to the simplification, security and efficiency improvement of products and services, and actively seek energy-saving solutions to reduce the impact of information and communication technology (ICT) growth on climate change, ensuring that ICT can generally improve the quality of life.
3. Content Delivery
Facing the trend of convergence of the Internet, mobile communications and broadcasting, we will solve the problem of inconsistent standards in different fields and promote the unification of cross-platform content transmission standards such as Internet Protocol Television (IPTV), mobile television and radio television, benefiting the industry and consumers.
4. Networks
In order to meet the needs of users to access communication services anytime, anywhere and on multiple devices, comprehensive access network technology standards are formulated to promote network integration.
5. Wireless Systems
Covering mobile phones, broadcasting, wireless LAN, cordless technology, global navigation satellite system (GNSS), radio frequency identification (RFID) and short-range wireless equipment, it formulates key wireless technology and system standards while providing spectrum management and harmonious coexistence between systems. Provide normative basis.
6. Transportation
Innovate the transportation industry through information and communication technology, improve efficiency, reliability and safety, reduce energy consumption, cover road, railway, aviation and maritime transportation, and respond to actual market needs.
7. Connecting Things
For the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), integrate radio frequency identification, machine-to-machine (M2M) service platform, wireless sensor network and other technologies to support smart devices, smart cities, smart grids, Internet of Vehicles, e-health, smart homes, energy management, public Security and remote industrial control and other applications.
8. Interoperability
Market-driven interoperability is a key element in a multi-vendor, multi-network, and multi-service environment. Standards are formulated to enhance user freedom of choice and promote manufacturers' economies of scale. They are the key to the successful promotion of modern technologies, especially the introduction of new technologies. Key factor.
9. Public Safety
Emphasizing the role of communication in emergencies, whether small-scale incidents or large-scale natural disasters, efficient communication support is required.
10. Security
Information security standards are essential to ensure interoperability between systems and networks, comply with laws and regulations, and achieve necessary security levels, laying the foundation for user protection and a safe and profitable environment in the industrial sector.
(3) Classification according to the technology involved
Chinese |
English |
3GPPTelecom management |
3GPP Telecom Management |
5G |
5G |
Aerospace |
Aeronautical |
AI |
Artificial Intelligence |
Augmented Reality |
Augmented Reality |
Automotive Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) |
automotive Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) |
Broadband cable access |
Broadband Cable Access |
Broadband Satellite Multimedia |
Broadband Satellite Multimedia |
Broadband wireless access |
Broadband Wireless Access |
broadcast |
Broadcast |
Certification authorities and other trust service providers |
Certification Authorities and other Trust Service Providers |
codec |
Codecs |
Consumer IoT Security |
Consumer IoT security |
cyber security |
Cybersecurity |
Digitally Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) |
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) |
digital signature |
Digital Signature |
DVB-S/S2/S2X |
DVB-S/S2/S2X |
eHealth |
eHEALTH |
electromagnetic compatibility |
Electro Magnetic Compatibility |
Energy efficiency and environmental aspects |
Energy efficiency and environmental aspects |
ETSItechnology radar- present and futureWork |
ETSI TECHNOLOGY RADAR - present & future work |
Experiential Network Intelligence (ENI) |
Experiential Networked Intelligence (ENI) |
Fifth generation fixed network (F5G) |
Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G) |
fixed radio link |
Fixed Radio Links |
fixed line access |
Fixed-line Access |
Galileo positioning system |
Galileo |
Human Factors Engineering(HF) and accessibility |
Human Factors (HF) and accessibility |
Integrated sensing and communications |
Integrated Sensing and Communications |
Internet of Things (IoT) |
Internet of Things (IoT) |
Lawful interception (LI) |
Lawful Interception (LI) |
Mobile lawful interception |
Lawful Interception for Mobile |
maritime communications |
Maritime |
medical equipment |
Medical devices |
Mobile and private mobile radio |
Mobile and Private Mobile Radio |
mobile communications |
Mobile Communications |
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) |
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) |
Network functions virtualization (NFV) |
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) |
NoIPnetwork(NIN) |
Non-IP Networking (NIN) |
Open source management and orchestration (OSM) |
Open Source MANO (OSM) |
Authorized distributed ledger (PDL) |
Permissioned Distributed Ledgers (PDL) |
Programming and Special Events (PMSE) |
Program making & special events (PMSE) |
Public Safety and Emergency Communications |
Public safety & emergency communications |
service quality |
Quality of Service |
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) |
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) |
Quantum safe encryption (QSC) |
Quantum-Safe Cryptography (QSC) |
radio communications |
Radio |
Railway communications (RT) |
Rail Communications (RT) |
Reconfigurable smart surfaces |
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces |
reconfigurable radio |
Reconfigurable Radio |
safety |
Safety |
Satellite Communications |
Satellite Communications |
Secure element (smart card) |
Secure Elements (Smart Cards) |
Securing artificial intelligence |
Securing Artificial Intelligence (SAI) |
security algorithm |
Security algorithms |
short range equipment |
Short Range Devices |
SIMCard |
SIM |
Smart home appliances andSAREF |
Smart appliances and SAREF |
intelligent body area network |
Smart Body Area Networks |
Smart City |
Smart cities |
Smart Grid and Smart Meter |
Smart Grids and Meters |
Terahertz (THz) |
Terahertz (THz) |
test language |
Testing languages |
TETRAstandard |
TETRA |
ultra wideband technology |
Ultra Wide Band |
digital subscriber line (xDSL) |
xDSL |
Zero-touch network and service management (ZSM) |
Zero touch network & Service Management (ZSM) |
Attachment 1: List of 50 standards recently released by ETSI
Attachment 2: List of the 50 most downloaded standards from ETSI



